Robotbit Edu can be programmed with KittenBlock.
Refer to this page for introduction with Kittenblock: Kittenblock Introduction
Navigation
00 - Robotbit Edu Introductions & FAQ
02 - Robotbit Edu Coding with MakeCode
03 - Robotbit Edu Coding with Kittenblock
Kittenblock Coding

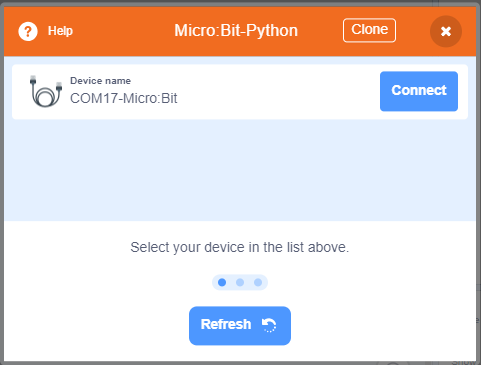
Connect the Micro:bit to your computer with a USB cable.
Click select hardware and choose MicroBit Python from the menu.
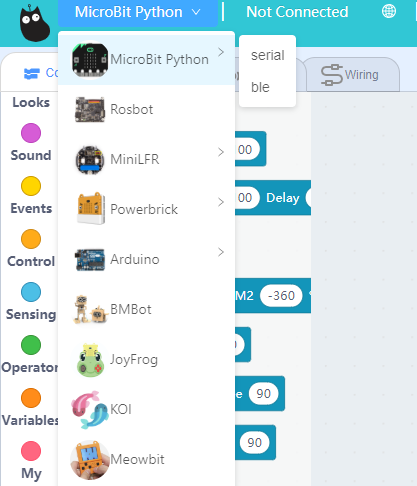
Press this exclamation mark(!).
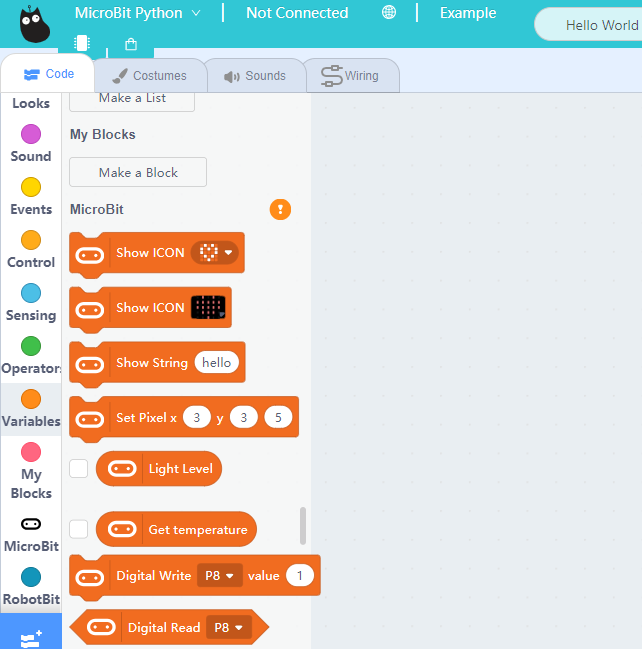
Click this button to connect the Micro:bit.
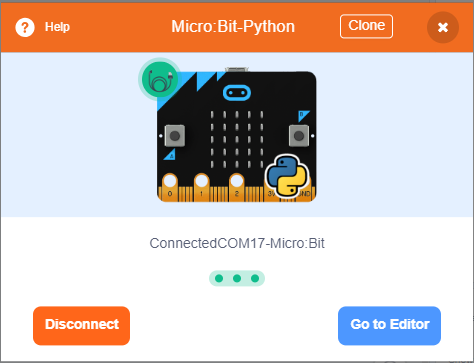
Micro:bit will display a heart icon after connecting to Kittenblock.
If the Micro:bit does not show a heart icon,

The blocks for Robotbit will be added
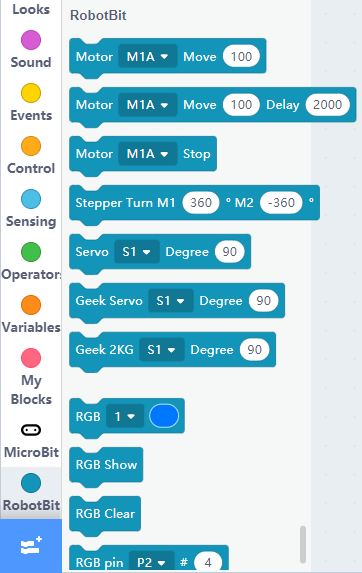
1. Programming Motors
For information about DC motors by Kittenbot, please visit: Kittenbot Actuators
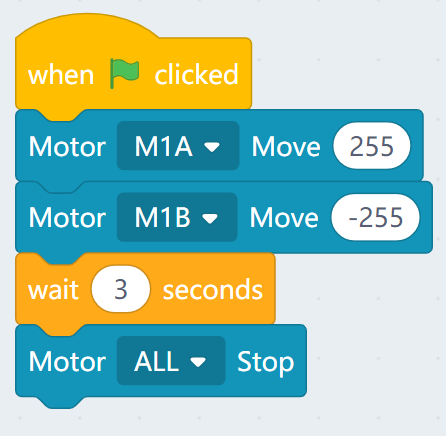
Sample Program:
Connect 2 DC motors to the M1A and M1B port of the Robotbit.
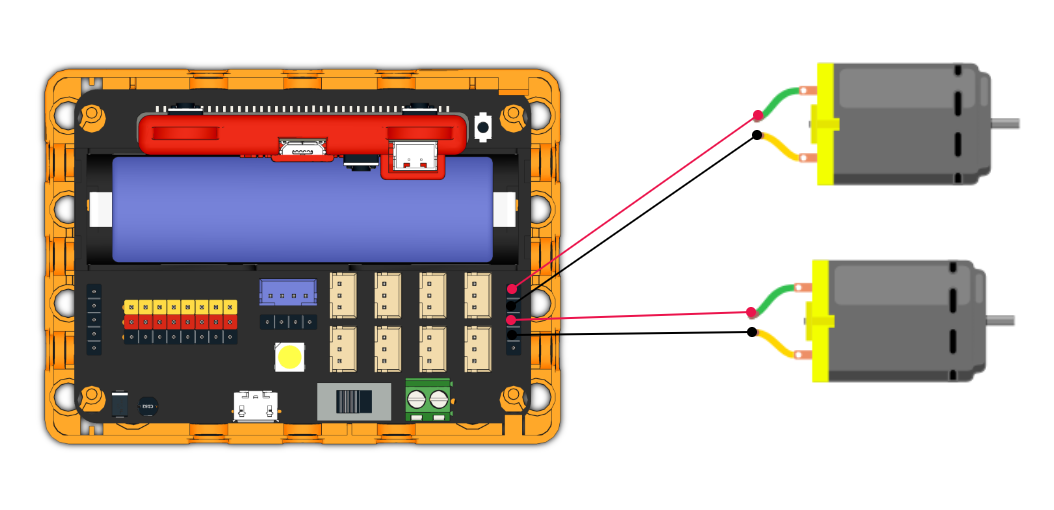
| The speed of motor ranges from -255 to 255. |
2. Programming Servos
For information about servos by Kittenbot, please visit: Kittenbot Actuators
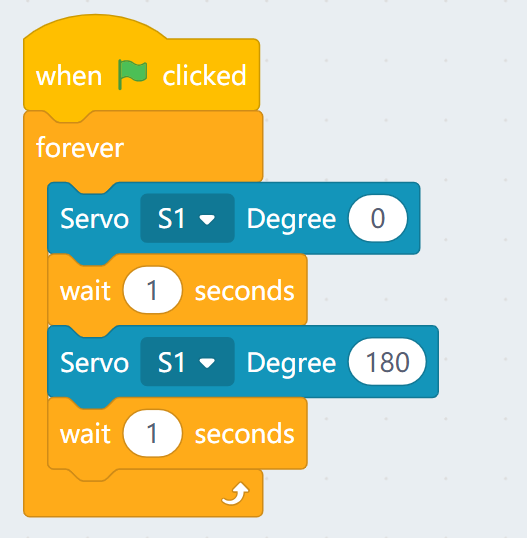
Sample Program:
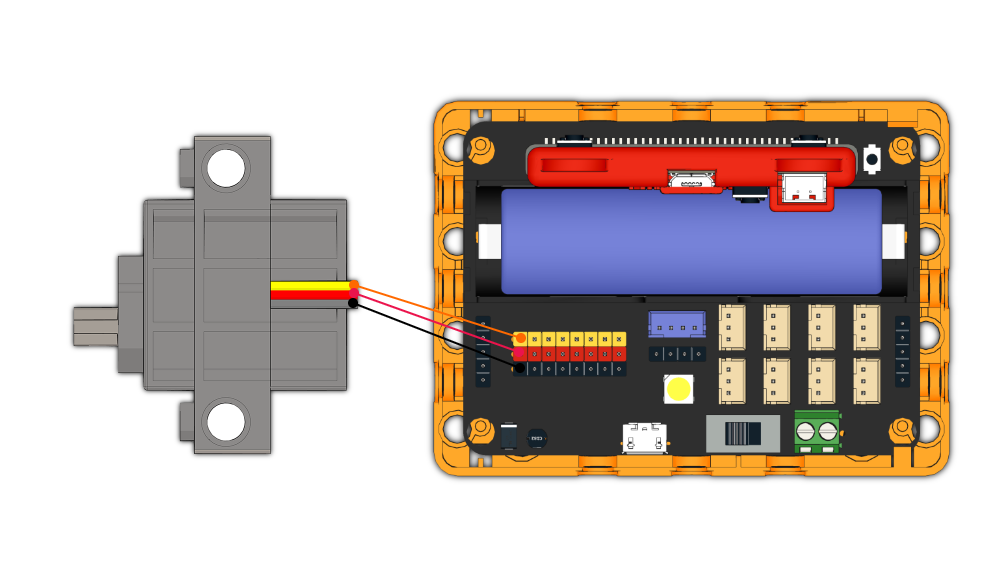
Connect a servo to the S1 port of Robotbit.
| Connect the orange wire from the servo to the yellow wire of the Robotbit. |
| Typical servos have a rotation range of 0-180. |
3. Programming Stepper Motors
For information about DC motors by Kittenbot, please visit: Kittenbot Actuators
Sample Program:
Connect Stepper Motors to the M1 and M2 port of the Robotbit, with the red wire connecting to the VM port.
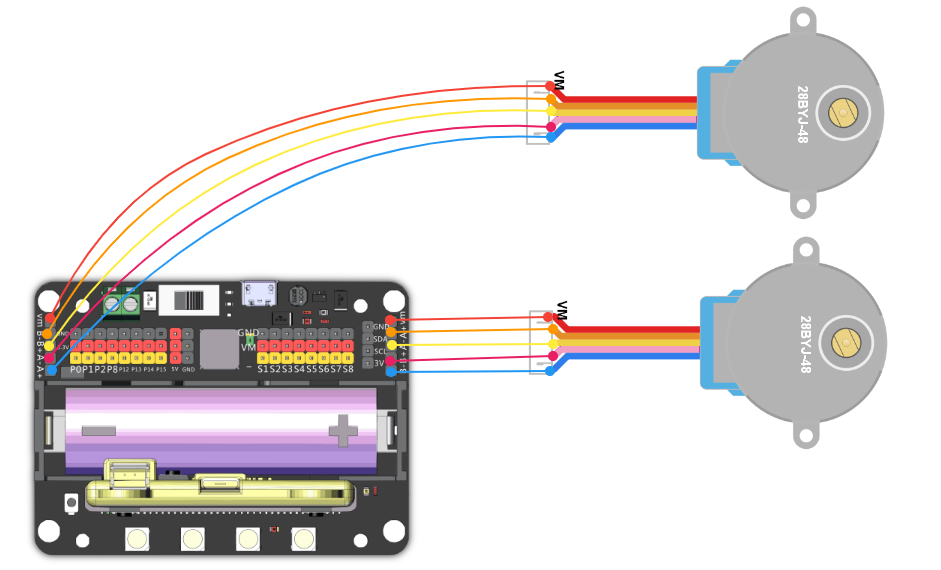
| Stepper Motors have a rotation range of -360 to 360. |
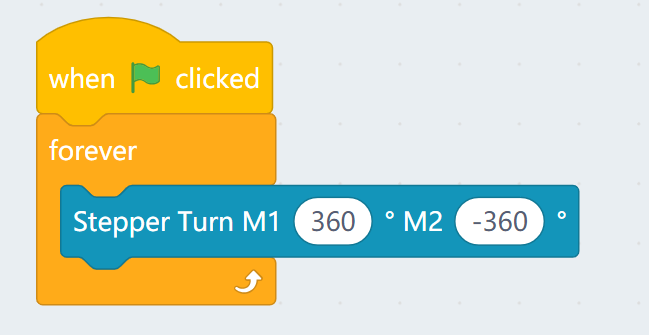
4. Programming the built-in LED strip
| Remember to add a "Show" block to display the effect. |
4.1 Lighting up all lights
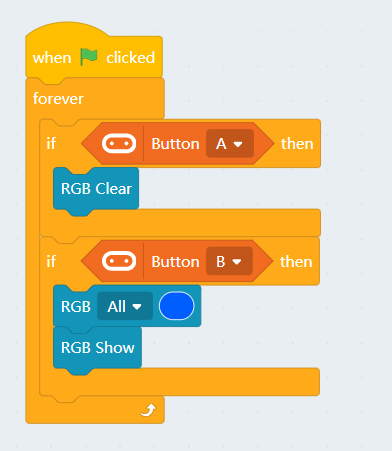
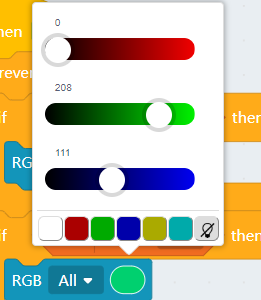
4.2 Customizing color with RGB
| RGB value has a range of 0-255. |
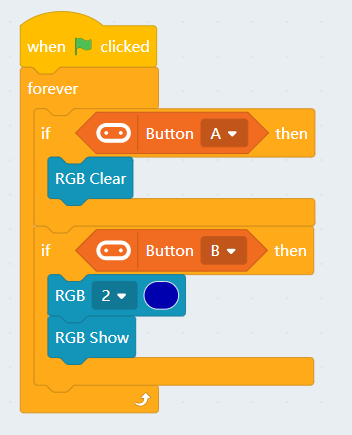
4.3 Lighting up individual lights
| The lights are labelled 0-3. (As labelled on the Robotbit) |
![]()
5. Programming the IO Pins
The blocks for the IO pins are found in the menu for Micro:bit.

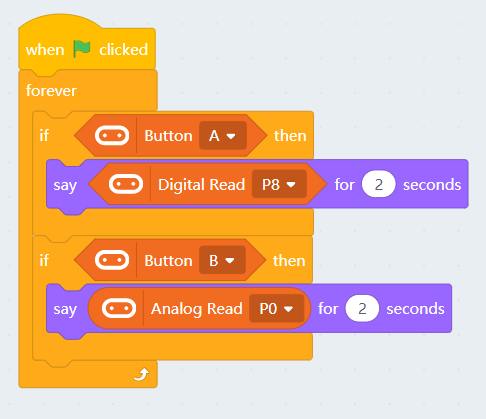
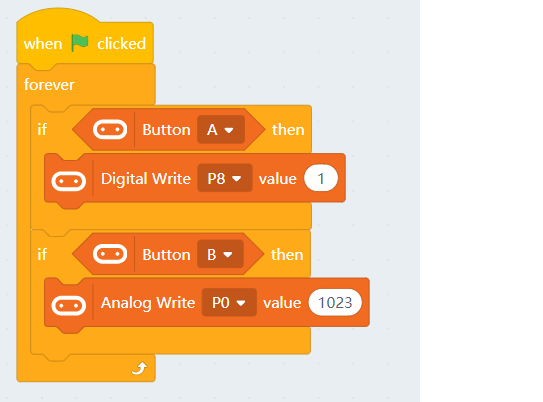
| Pin 0-2 can be used as analog pins while P8, P12~P15 can only be used as digital pins. Analog values have a range of 0 to 1023, digital values have a range of 0 to 1. |

5.1 Reading values from pins
| Pin 0 is occupied by the buzzer by default, the jumper should be removed when using this pin. |
5.2 Writing values to pins
| Pin 0 is occupied by the buzzer by default, the jumper should be removed when using this pin. |
If you have any question, please feel free to contact us at Discord, we will always be there to help.
KittenBot Team